Many people lack awareness of the seriousness of skin cancer. Therefore they neglect regular skin examination by a dermatologist.
People are often unaware of the drastic consequences of sunbathing without UV protection and underestimate the serious impact on the health of their skin. Moles change over time and due to environmental influences.
This includes dangerous UV radiation from the sun, which has been proven to cause skin cancer.
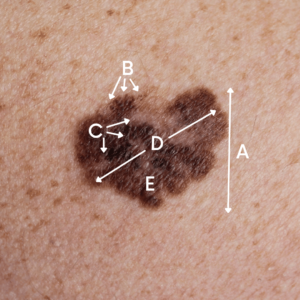
There are several evidences that can indicate whether a mole is benign or malignant. The great advantage of skin cancer compared to other types of cancer is that skin cancer usually develops on the surface of the skin and can therefore be seen and felt.
For laymen, the detection of skin cancer is more difficult than for specialists. However, even non-experts can detect skin cancer with the help of a few tips and by regular self-examination .
The appearance of skin cancer is very diverse and each type of cancer has its individual characteristics. Both malignant and non-malignant skin cancer are visible on the surface of the skin. The following photo series with pictures of malignant skin cancer, known in technical language as malignant melanoma should help you to recognize it.
Every 7 minutes someone receives the diagnosis malignant melanoma.
What does melanoma skin cancer look like?
Melanomas can look different and can develop anywhere on the body. They change in color, shape and size over time.
Malignant melanoma has typical visual characteristics. The color gradient can be irregular, ranging from brown to black, and in rare cases can be reddish or white.
Look for anything new on the skin, changing, or unusual on both sun-exposed and sun-protected areas of the body.
However, remember that melanomas can develop anywhere on the skin, even in places where the sun doesn’t shine and which are themselves difficult to see.
Please note: Since not all melanomas look the same, these photos serve as a general guide to what a malignant melanoma may look like. If you see anything new, different or unusual on your skin, get it checked out by a dermatologist.






Copyright: all above photos were taken by LKH-Univ. Klinikum Graz provided and diagnosed.
Melanomas often occur on the legs in women, while in men they are mainly found on the torso.
Causes and risk factors for malignant skin cancer
Some people have naturally at greater risk of developing skin cancer. The reasons for this can be very different but do not change the fact that these people should especially protect themselves from too intense sun exposure.
- People who are naturally pale, blond or red-haired, have freckles and many moles belong to the risk group.
- People who have many and large moles also have an increased risk.
- People who had sunburns in childhood and adolescence have a two- to three times increased risk of skin cancer.
- People who regularly go to the solarium also have an increased risk.
- People who have a weakened immune system are at risk.
- People who have had skin cancer cases in their family have an increasing risk of skin cancer.
If anything seems suspicious or you have doubts about whether a mole is benign, ask a doctor you trust. This is best done immediately. A regular skin and birthmark check is especially important to detect malignant skin cancer as early as possible.